Table of Contents
A Revolution in the Bedroom
In recent years, the sex toy industry has seen a surge in popularity of customisable sex toys, including 3D printed sex toys, with the global market expected to reach £23.9bn by 2025 [1]. A significant driver of this growth is the increasing acceptance of sex toys like Wand Massagers as a normal and healthy part of adult life. However, as with many industries, advances in technology are disrupting the status quo, and 3D printing has emerged as a force to be reckoned with. Could 3D printing signal the end of the traditional sex toy industry?
A Background on 3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a process that creates three-dimensional objects by adding layers of material on top of one another. The technology has been around since the 1980s, but in recent years, it has become increasingly affordable and accessible to the general public [2]. 3D printing has already transformed several industries, from manufacturing to healthcare, but its potential impact on the sex toy industry is only just beginning to be realised.
Customisation and Personalisation: The Appeal of 3D Printed Sex Toys
At first glance, it might seem strange to connect 3D printing with sex toys, but the two are a natural fit for several reasons.
One of the key factors driving the popularity of 3D printed sex toys is the ability to customise and personalise items to suit individual preferences and needs [3]. Traditional sex toy manufacturing relies on mass production, which often results in a limited range of shapes, sizes, and materials to choose from. In contrast, 3D printed sex toys offer consumers the opportunity to create products that are tailored to their specific desires, ensuring a more satisfying and comfortable experience.
Using 3D printing technology, consumers can adjust the dimensions, textures, and features of their sex toys to create a one-of-a-kind item that caters to their unique requirements. This level of customisation has the potential to revolutionise the way people approach their sexual pleasure, making 3D printed sex toys an increasingly attractive option for many [3].
Materials and Manufacturing: Silicone and Beyond
When it comes to 3D printed sex toys, silicone is the most common material used due to its body-safe, non-porous, and hypoallergenic properties [4]. Advances in silicone 3D printing technology have made it possible to produce intricate designs and details, resulting in more diverse and innovative products. Furthermore, silicone 3D printed sex toys can be produced in a range of colours, textures, and firmness levels, allowing consumers to customise their products to their liking [4].
However, 3D printed sex toys can also be produced using other materials, such as plastic, metal, and even glass [5]. The choice of material can impact the overall user experience, as well as the safety and durability of the product. As the industry continues to evolve, it is likely that new materials and manufacturing techniques will emerge, further expanding the possibilities for 3D printed sex toys [6].
Privacy and Discretion: The Allure of DIY 3D Printed Sex Toys
Another reason behind the growing interest in 3D printed sex toys is the appeal of privacy and discretion. With the ability to print sex toys at home or at local maker spaces, consumers can bypass traditional retail channels and avoid potential embarrassment or stigma associated with purchasing such products in person or online [5]. This DIY approach to 3D printed sex toys has made it easier for individuals to explore their sexuality and experiment with new products in a private and discreet manner.
Online platforms such as Cults [7] and Lovehoney [8] offer digital files and templates that can be downloaded and printed at home, making it simple for users to create their own custom 3D printed sex toys. Furthermore, 3D printing technology has the potential to reduce the cost of sex toys, making them more accessible to a wider audience [9].
Intellectual Property and Legal Concerns: The Dark Side of 3D Printed Sex Toys
While the rise of 3D printed sex toys offers many exciting opportunities, it also raises several legal and intellectual property (IP) concerns. As individuals gain the ability to create and share digital designs for 3D printed sex toys, there is an increased risk of copyright infringement and counterfeiting [10]. For example, unscrupulous individuals may replicate and distribute designs without the original creator’s consent, leading to potential losses in revenue and damage to the creator’s reputation.
Moreover, 3D printed sex toys that are based on the likeness of real people or fictional characters may also raise privacy and IP issues. In some cases, these concerns have led to legal disputes and challenges, highlighting the need for clear regulations and guidelines surrounding the production and distribution of 3D printed sex toys [11].
To address these issues, industry experts and legal professionals have called for the development of a comprehensive regulatory framework that addresses the unique challenges posed by 3D printed sex toys. Such a framework would need to balance the rights of creators and manufacturers with the interests of consumers, while also ensuring the safety, quality, and legality of these products [13].
Safety and Quality Control: Ensuring the Well-Being of Users
As with any product designed for intimate use, safety and quality control are critical concerns for 3D printed sex toys. When creating a 3D printed sex toy, it is important to consider factors such as the material used, the smoothness and integrity of the printed surface, and the overall design and structure of the item [12]. Ensuring that 3D printed sex toys are made from body-safe materials and are free from defects or sharp edges is essential for protecting the health and well-being of users.
While 3D printing technology has made it easier for individuals to create their own custom sex toys, it has also raised concerns about the potential for substandard or unsafe products to enter the market. To mitigate these risks, experts recommend that consumers educate themselves about the materials and processes used in 3D printing and purchase products from reputable sources or manufacturers [12]. Additionally, some industry professionals have called for the establishment of safety standards and certification processes for 3D printed sex toys, similar to those in place for traditional sex toy manufacturing [13].
The Future of Sex Toys and 3D Printing: A Brave New World
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, it is likely that we will see further developments and innovations in the realm of 3D printed sex toys. From increased customisation and personalisation to improved materials and manufacturing processes, the potential for growth and change within this industry is immense [9].
However, to fully realise the potential benefits and opportunities offered by 3D printed sex toys, it will be necessary to address the various challenges and concerns that have emerged, including safety, quality control, IP rights, and regulatory issues. By working together to develop and implement effective solutions, industry stakeholders, legal professionals, and consumers can help to shape the future of 3D printed sex toys and ensure that this exciting technology continues to thrive and evolve.
The Disruption of an Industry
As more and more consumers turn to 3D printing to create their own sex toys, traditional manufacturers may find their market share dwindling. Already, a number of websites have emerged offering free or low-cost 3D designs for sex toys, which can be downloaded and printed at home or through a 3D printing service [7].
In response to this new competition, some established sex toy companies have started to embrace 3D printing technology themselves. For example, the UK-based company Lovehoney has released a line of 3D printed sex toys, claiming that their products offer a higher level of customisation and quality compared to those made using traditional manufacturing methods [8].
However, not all industry players are embracing this new technology with open arms. Some argue that the rise of 3D printed sex toys poses a threat to the livelihood of traditional manufacturers and retailers, who may struggle to compete with the low cost and customisation offered by 3D printing [9]. There is also the question of intellectual property rights, as it becomes increasingly difficult to protect unique designs and innovations in an environment where anyone can download and print a sex toy [10].
The Future of Sex Toys and 3D Printed Sex Toys
It remains to be seen whether 3D printing will completely upend the sex toy industry, but there is no denying that it has the potential to change the landscape dramatically. As technology continues to advance and become more accessible, it is likely that we will see a growing number of consumers turning to 3D printing for their sex toy needs.
For traditional manufacturers, this may mean a need to adapt and innovate in order to remain competitive. This could involve adopting 3D printing technology, as Lovehoney has done, or focusing on other aspects of the business, such as branding, customer service, and product quality. It is also possible that we may see a rise in collaborations between traditional manufacturers and 3D printing companies in a bid to combine the best of both worlds.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Another aspect to consider when examining the impact of 3D printing on the sex toy industry is the environmental implications. Traditional manufacturing processes often involve the production of large quantities of waste, significant energy consumption and the release of harmful emissions. With 3D printing, however, there is the potential to reduce waste, energy use, and emissions by producing items on a smaller scale and on demand [14].
Moreover, the ability to create customised sex toys could also result in fewer products being discarded or replaced, as consumers may be more likely to hold onto items tailored to their specific needs and desires. In addition, advancements in 3D printing materials have led to the development of biodegradable and eco-friendly options, which could further reduce the environmental footprint of sex toy production [15].
Despite these potential benefits, it is important to recognise that 3D printing is not without its own environmental challenges. For example, the energy consumption of some 3D printers can be quite high, particularly when used for extended periods [16]. Furthermore, the disposal of waste materials generated during the 3D printing process, such as support structures and failed prints, must also be considered. To fully realise the potential environmental advantages of 3D printed sex toys, it will be necessary for both manufacturers and consumers to adopt sustainable practices and make conscious choices about the materials and processes they use.
Economic Implications and Job Opportunities
While some critics argue that the rise of 3D printed sex toys could lead to job losses within the traditional manufacturing sector, it is also worth considering the potential economic benefits and new job opportunities that this technology could bring. For example, the growth of 3D printing has led to an increase in demand for skilled designers and engineers who can create and optimise digital models for printing [17].
Additionally, as more people become interested in 3D printing their sex toys, there may be a surge in demand for 3D printing workshops, classes, and services, creating new avenues for income and employment. Local 3D printing hubs, where individuals can access printers and resources, could stimulate local economies and foster community engagement [18].
Furthermore, adopting 3D printing within the sex toy industry could pave the way for innovative start-ups and entrepreneurs to enter the market. By utilising this technology, small businesses can quickly iterate on their designs and bring unique, customised products to market without needing large-scale manufacturing facilities [19]. This could ultimately contribute to greater diversity and innovation within the industry, as well as increased competition and economic growth.
The Importance of Safety and Quality Control
As the popularity of 3D printed sex toys continues to grow, both consumers and manufacturers alike must be aware of the potential risks associated with their use. One key concern is the issue of safety and quality control, as not all 3D printed materials are suitable for intimate use [11].
When creating a 3D printed sex toy, it is essential to use body-safe materials, such as medical-grade silicone, and ensure that the toy is thoroughly cleaned and sterilised before use. Additionally, the design should be carefully considered to avoid sharp edges or protrusions that could cause injury [12].
Regulation and oversight of 3D printed sex toys is another area that needs attention. Currently, there are no specific regulations governing the production and sale of 3D printed sex toys, which means that consumers may be at risk of purchasing a product that is unsafe or of poor quality [13]. To protect the public, it may be necessary for governments and regulatory bodies to introduce new legislation or guidelines specific to this emerging market.
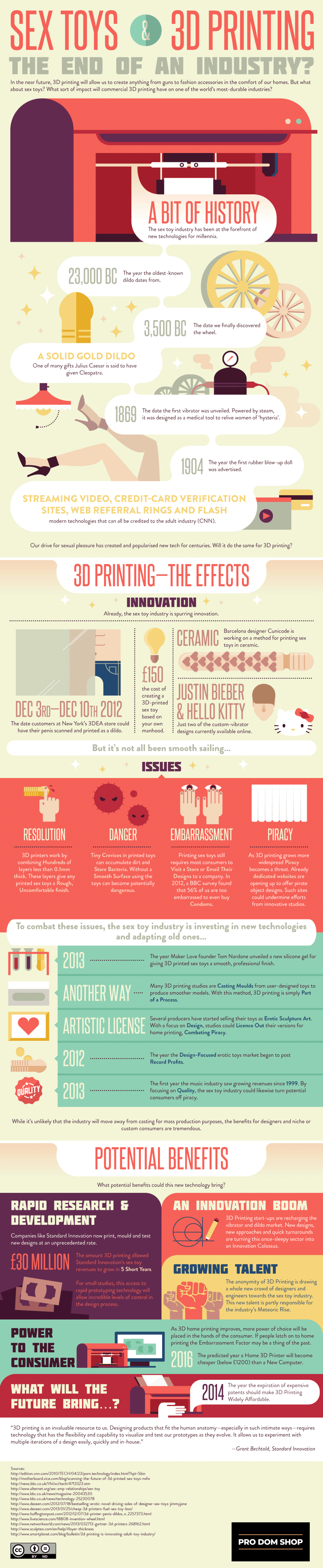
History of Sex Toys: Info-Graphic
The oldest sex toy found by archaeologists was dated back to 23,000 BC. Julius Cesar is said to have given Cleopatra a solid gold dildo…
Conclusion
3D printing has the potential to revolutionise the sex toy industry, offering consumers greater choice, customisation, and privacy than ever before. However, this new technology also brings a range of challenges and concerns, from the threat to traditional manufacturers to the importance of ensuring safety and quality control.
As we look to the future, it is clear that the sex toy industry must adapt and evolve to keep pace with the rapid advances in 3D printing technology. Whether this spells the end of the industry as we know it or simply ushers in a new era of innovation and collaboration remains to be seen.
What do you think?
Comment below to get the conversation started…
Sources & References
[1] Technavio, “Global Sex Toys Market 2021-2025,” 2021. https://www.technavio.com/report/sex-toys-market-industry-analysis
[2] T. Wohlers, “Wohlers Report 2021: 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing State of the Industry,” Wohlers Associates, 2021. https://wohlersassociates.com/2021report.htm
[3] B. Khullar, “Customisable 3D Printed Sex Toys: The Future of Personalisation,” Future of Sex, 2021. https://futureofsex.net/sex-tech/customisable-3d-printed-sex-toys-the-future-of-personalisation
[4] J. Boudin, “Silicone 3D Printing: How to 3D Print Silicone,” All3DP, 2021. https://all3dp.com/2/silicone-3d-printing-how-to-3d-print-silicone/
[5] A. Grant, “The Discreet Future of Sex Toys: 3D Printing,” Forbes, 2020. https://www.forbes.com/sites/andreagrant/2020/08/19/the-discreet-future-of-sex-toys-3d-printing/
[6] M. Stevens, “3D Printing Sex Toys: The Benefits and Drawbacks,” 3D Insider, 2021. https://3dinsider.com/3d-printing-sex-toys/
[7] Cults, “Sex Toys 3D Models,” 2021. https://cults3d.com/en/categories/sex-toys
[8] Lovehoney, “3D Printed Sex Toys,” 2021. https://www.lovehoney.co.uk/3d-printed-sex-toys
[9] L. Young, “How 3D Printing is Changing the Sex Toy Industry,” Vice, 2020. https://www.vice.com/en/article/n7wq37/how-3d-printing-is-changing-the-sex-toy-industry
[10] A. Cimpan, “Intellectual Property and 3D Printing: A Case Study,” 3D Printing Industry, 2020. https://3dprintingindustry.com/news/intellectual-property-and-3d-printing-a-case-study-172153/
[11] S. Farnsworth, “The Safety of 3D-Printed Sex Toys: What You Need to Know,” Kinkly, 2021. https://www.kinkly.com/the-safety-of-3d-printed-sex-toys-what-you-need-to-know/2/16849
[12] J. Bell, “Safety Considerations for 3D Printed Sex Toys,” SexTechGuide, 2020. https://sextechguide.com/features/safety-considerations-for-3d-printed-sex-toys/
[13] M. Jones, “Regulating 3D Printed Sex Toys: A Legal Perspective,” 3DPrint.com, 2019. https://3dprint.com/243424/regulating-3d-printed-sex-toys-a-legal-perspective/
[14] T. Gutowski, et al., “Environmental Life Cycle Analysis of Distributed Three-Dimensional Printing and Conventional Manufacturing of Polymer Products,” ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00646
[15] J. Boudin, “Eco-Friendly 3D Printing: Filaments, Facts, and the Future,” All3DP, 2021. https://all3dp.com/2/eco-friendly-3d-printing-filaments-facts-and-the-future/
[16] M. Kreiger, et al., “Environmental Impacts of Distributed Manufacturing from 3-D Printing of Polymer Components and Products,” MRS Energy & Sustainability, 2018. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/mrs-energy-and-sustainability/article/environmental-impacts-of-distributed-manufacturing-from-3d-printing-of-polymer-components-and-products/62C931E71F7A0A7515F5A9D2B13A7290
[17] R. Jones, “The Role of 3D Printing in Job Creation,” 3DPrint.com, 2020. https://3dprint.com/270699/the-role-of-3d-printing-in-job-creation/
[18] L. Rouhiainen, “How 3D Printing is Transforming Local Economies,” 3DPrintingIndustry.com, 2020. https://3dprintingindustry.com/news/how-3d-printing-is-transforming-local-economies-168474/
[19] K. Weller, “How 3D Printing is Empowering SMBs in Manufacturing’s Digital Transformation,” Forbes, 2020. https://www.forbes.com/sites/kaylieweller/2020/01/31/how-3d-printing-is-empowering-smbs-in-manufacturings-digital-transformation/